
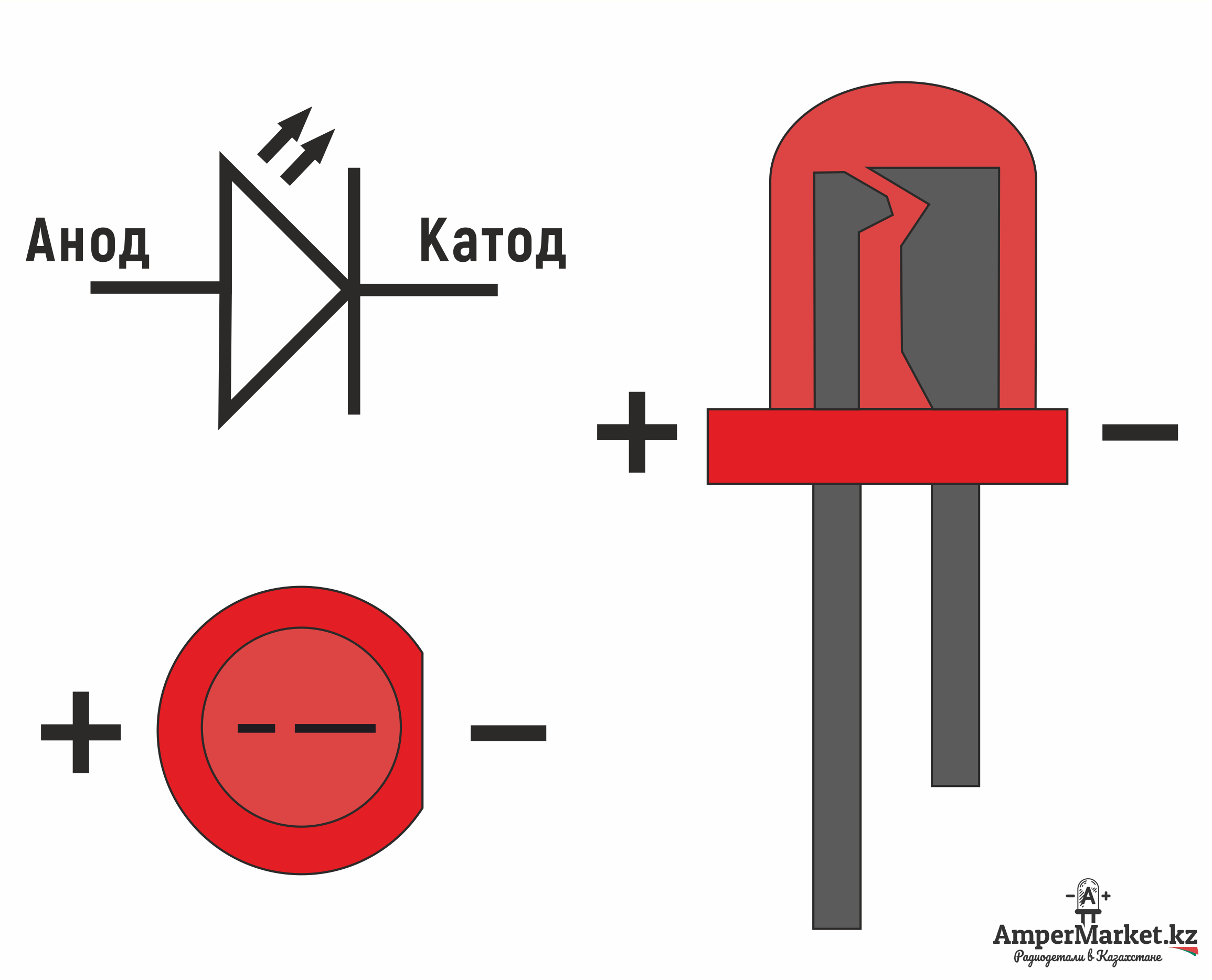
In a diode, the cathode is the negative terminal at the pointed end of the arrow symbol, where current flows out of the device. For example, reversing the current direction in a Daniell galvanic cell converts it into an electrolytic cell where the copper electrode is the positive terminal and also the anode.
#ANODE CATHODE PIC GENERATOR#
For example, the Daniell galvanic cell's copper electrode is the positive terminal and the cathode.Ī battery that is recharging or an electrolytic cell performing electrolysis has its cathode as the negative terminal, from which current exits the device and returns to the external generator as charge enters the battery/ cell. It is continued externally by electrons moving into the battery which constitutes positive current flowing outwards. This outward current is carried internally by positive ions moving from the electrolyte to the positive cathode (chemical energy is responsible for this "uphill" motion). Whether the cathode is negatively polarized (such as recharging a battery) or positively polarized (such as a battery in use), the cathode will draw electrons into it from outside, as well as attract positively charged cations from inside.Ī battery or galvanic cell in use has a cathode that is the positive terminal since that is where conventional current flows out of the device. Inside a device or a cell, positively charged cations always move towards the cathode and negatively charged anions move towards the anode, although cathode polarity depends on the device type, and can even vary according to the operating mode. The electrode through which conventional current flows the other way, into the device, is termed an anode.Ĭonventional current flows from cathode to anode outside of the cell or device (with electrons moving in the opposite direction), regardless of the cell or device type and operating mode.Ĭathode polarity with respect to the anode can be positive or negative depending on how the device is being operated. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode. Consequently, the mnemonic cathode current departs also means that electrons flow into the device's cathode from the external circuit. Electrons have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is opposite to that of the conventional current flow. A conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic CCD for Cathode Current Departs. Positively charged cations move towards the cathode allowing a positive current i to flow out of the cathode.Ī cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. It does not store any personal data.Electrode where reduction takes place Diagram of a copper cathode in a galvanic cell (e.g., a battery). The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other.

The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
